How to understand which vitamins lack in the body; Diseases with a lack of vitamins
Find out what exactly the vitamins in the body are not enough – easy! Get acquainted with signs of lack of vitamins and help yourself fill the lack of vitamins. Find out what diseases may occur when the vitamins lack

Vitamins are those valuables by which we have the opportunity to cheerfully and correctly walk through life, and do not lie in bed, loosen from various diseases. The disadvantage of this or that vitamin always indicates a failure in the body, and its irrelevant leads to even greater ailments. How to find out – what kind of vitamin the body is missing, what to fill the lack of vitamins, and what it threatens with inaction?
The main signs of lack of vitamins – test your body!
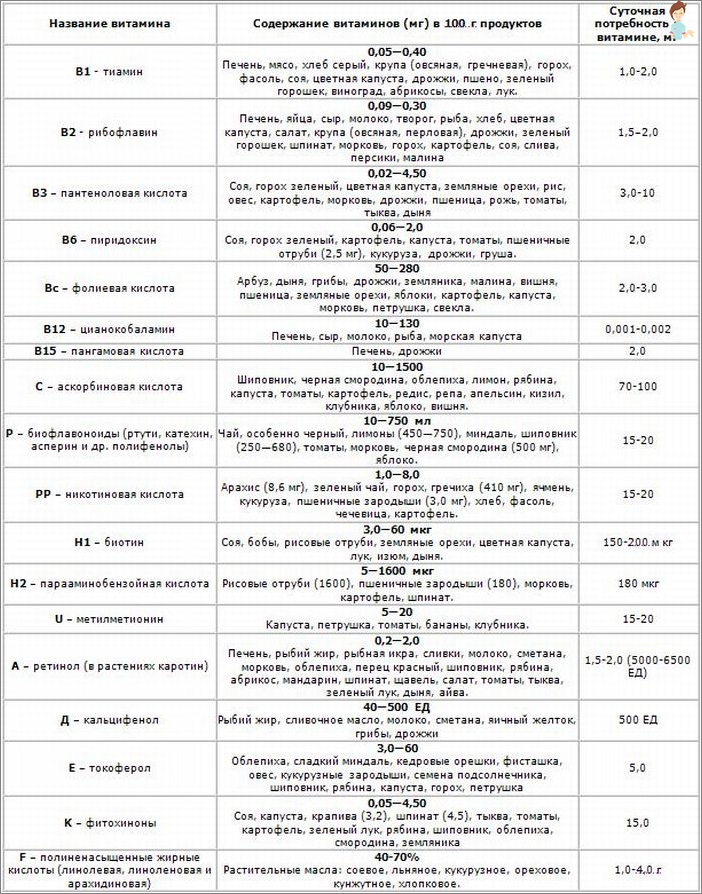
Tables 1.2: The main symptoms of the lack of vitamins and trace elements in the human body
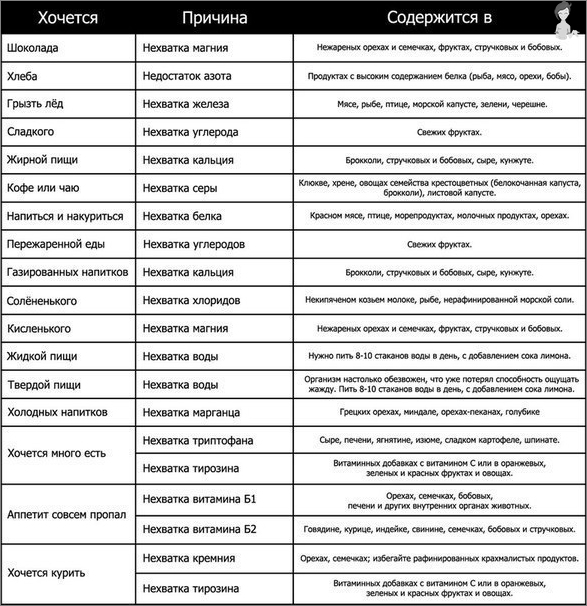
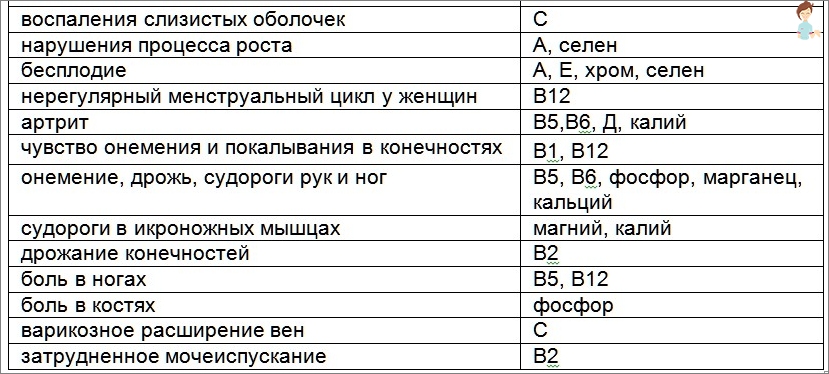
What kind Symptoms appear when the lack of one or another vitamin?
-

Vitamin A deficiency:
dryness, fragility, hair thinning; Nail fragility; the appearance of cracks on the lips; damage to mucous (trachea, mouth, gastrointestinal tract); reduction of vision; Raw, dry skin and peeling. - Vitamin B1 deficiency:
diarrhea and vomiting; gastrointestinal disorders; decline in appetite and pressure; increased excitability; Cardiac arrhythmia; Cold limbs (circulatory disorders). - Vitamin B2 deficiency:
Stomatitis and cracks in the corners of the mouth; conjunctivitis, tearing and reduced vision; Voring the cornea of the eye and lightness, dry mouth. - Vitamin B3 deficiency:
weakness and chronic fatigue; regular headaches; anxiety and nervousness; Increased pressure. - Vitamin B6 deficiency:
weakness; sharp deterioration in memory; soreness in the field of liver; dermatitis. - Vitamin B12 deficiency:
anemia; glossitis; hair loss; gastritis. - Vitamin C:
general weakness against the background of immunity reduction; weight loss; bad appetite; bleeding gums and caries; exposure to colds and bacterial infections; bleeding from the nose; unpleasant. - Vitamin D deficiency:
In children – lethargy and low-passability; sleep disorders and bad appetite; capriciousness; rickets; reduction of immunity and vision; metabolic disease; Problems with bone tissues and skin. - Vitamin D3 deficiency:
Poor absorption of phosphorus / calcium; Later teething; Sleep disorders (gravity, shudding); reduced muscle tone; Fragility bones. - Vitamin E deficiency:
a tendency to allergies of various kinds; muscle dystrophy; Pain in the legs due to impaired nutritional nutrition; the appearance of trophic ulcers and the development of thrombophlebitis; Changes in gait; The appearance of pigment spots. - Vitamin K:
Violations in the work of the GCT; diseases of menstruation and cycle disorders; anemia; fast fatiguability; bleeding; Hemorrhage under the skin. - Vitamin R deficiency:
The appearance of point hemorrhages on the skin (especially in places pulled by cramped clothing); Pain in legs and shoulders; Total lethargy. - Vitamin RR deficiency:
apathy; dysfunction gastrointestinal peeling and dry skin; diarrhea; inflammation of the mucous meal and language; dermatitis; headaches; fatigue; fast fatiguability; Dry lip. - Vitamin N deficiency:
The appearance of a grayish skin shade; baldness; exposure to infections; muscle pain; Depressive states.
What will happen if not to fill the loss of vitamins: serious diseases with a lack of vitamins
To what diseases There is a disadvantage of this or that vitamin:
- «BUT»:

To hemerahopia, dandruff, a decrease in libido, chronic insomnia.
- «WITH»:
To losing hair (alopecia), long-term healing of wounds, periodontal disease, nervous disorders. - «D»:
to chronic insomnian, weight loss and vision. - «E»:
to muscle weakness, reproductive dysfunction. - «N»:
to anemia, depression, alopecia.
- «TO»:
To the problems of the pancreas and the gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis, diarrhea. - «Pp»:
to chronic fatigue and insomnia, depression, skin problems. - «IN 1»:
to constipation, reduction in vision and memory, weight loss. - «AT 2»:
To the angular stomatitis, the problems of the gastrointestinal tract, hair loss, headaches. - «AT 5»:
to depression, chronic insomnia. - «AT 6»:

to dermatitis, inhibition, depression.
- «AT 9»:
Early awareness, to a deterioration in memory, to digestion disorders. - «AT 12»:
to Malokrovia, reproductive dysfunction. - «B13»:
To diseases of the liver. - «U»:
To the problems of the tract.
Table of content of vitamins in food products: how to prevent lack of vitamins A, B, C, D, E, F, H, K, PP, P, N, U
In which products need to look for the necessary vitamins?
- «BUT»:

in citrus and spinach, crackle liver, butter, calamine and egg yolk, in sorrel, sea buckthorn, green onions, cream, broccoli, cheese, asparagus, carrots.
- «WITH»:
In Kiwi and citrus, in cauliflower and broccoli, in green vegetables, Bulgarian pepper, apples and melons, in apricots, peaches, rosehip, greenery and black currant. - «D»:
In fish oil, parsley and egg yolk, dairy products and butter creamy, beer yeast, proprieties of wheat, milk. - «N»:
in yolk, yeast, kidneys and liver, mushrooms, spinach, beets and cabbage. - «E»:
in vegetable oil and almond, sea buckthorn, crude crochets, sweet peppers, peas, apple seeds. - «TO»:
in cabbage and tomatoes, pumpkins, legumes and grain, pork liver, salad, alfalfa, rosehip and nettle, in cauliflower, green vegetables. - «R»:
In black currant and gooseberries, cherry, cherry and cranberries. - «Pp»:
in the liver, eggs, meat, greenery, nuts, fish, dates, rosehips, grain, white mushrooms, yeast and sorrel. - «IN 1»:
In untreated rice, coarse bread, yeast, egg squirrel, hazelnut, oatmeal, beef and legumes. - «AT 2»:
in broccoli, germinated wheat, cheese, oats and rye, soy, in the liver. - «AT 3»:
In eggs, yeast, sprouted grain. - «AT 5»:
in meat chicken, heart and liver, mushrooms, yeast, beets, cauliflower and asparagus, fish, rice, legumes, beef. - «AT 6»:
in cottage cheese and buckwheat, liver, potato, liver cod, yolk, heart, in milk, oysters, bananas, walnuts, avocado and corn, cabbage, salad, cabbage. - «AT 9»:
in melon, dowels, greenery, green peas, mushrooms, pumpkins, nuts and oranges, carrots, buckwheat, salad, fish, cheese and yolk, in milk, coarse flour. - «AT 12»:
in sea cabbage, calf liver, soy, oysters, yeast, fish and beef, herring, cottage cheese. - «AT 12»:
in Kumyes, milk, dairy products, liver, in yeast.
Table 3: Vitamins content in food