Reasons and signs of fainting, first aid – what to do when fainting, and what should not be done
How to help with fainting? The main reasons for fainting – from what fainted. Signs and symptoms of fainting. What to do with fainting, fainting rules for fainting – on Lady-Magazine.Com
Fainting – protective brain reaction. Just like this method of the brain, feeling the sharp lack of oxygen, trying to correct the situation. I.e, «places» body in horizontal position to facilitate the work of the heart for blood flow in the brain. As soon as the oxygen deficiency is replenished, the person returns to normal. What are the reasons for this phenomenon that precedes fainting, and how to give first aid?
What kind of fainting than dangerous and what it happens – the main causes of fainting
All known phenomenon – fainting is the loss of consciousness on a very short period, from 5-10 seconds to 5-10 minutes. Fainting that continued for a longer time is already dangerous for life.
What is dangerous fainting?
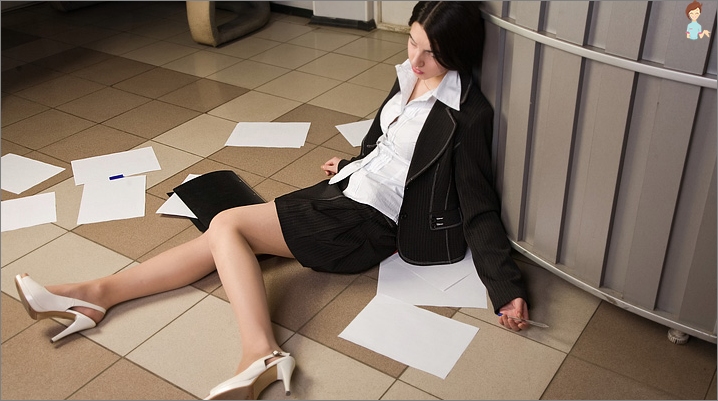

Single trimming episodes, inherently not dangerous for life. But there are reasons for anxiety if fainting ..
- Is a manifestation of any dangerous disease (heart pathology, heart attack, arrhythmia, etc.).
- Accompanied by a head injury.
- Occurs in a person whose activity is associated with sports, driving of a car, aircraft management, etc.
- Repeats from time to time or regularly.
- It happens in an elderly person – without visible causes and suddenly (there is a risk of full blockade of the heart).
- Accompanied by the disappearance of all reflexes of swallowing and breathing. There is a risk that the root of the language due to the relaxation of the muscular tone will be stock and block the respiratory tract.
Fainting – As a reaction to the smell of paint or from the type of blood is not so dangerous (except for the risk of injury during the fall). Much more dangerous if fainting – symptom of disease or nervous disorder. Do not pull on a visit to the doctor. The necessary specialists are a neurologist, a cardiologist and a psychiatrist.
Possible reasons for fainting – many. Basic, most common «Trigger mechanisms»:
- Short-term sharp decline in pressure.
- Long standing (especially if knees, «At the counter Smirno»).
- Long-flowing in one pose (sitting, lying) and a sharp rise to the feet.
- Overheating, heat / sunshine.
- Duchot, heat and even too bright light.
- Status of hunger.
- Strong fatigue.
- Increased temperature.
- Emotional stress, spiritual shock, fright.
- Acute sudden pain.
- Strong allergic reaction (for medicines, in insect bites, etc.).
- Hypotension.
- Reaction to medication at elevated pressure.
- Arrhythmia, anemia or glycemia.
- Infectious disease of the ear.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Menstruation offensive (girls).
- Pregnancy.
- Violations of the vegetative nervous system.
- Crowd, impressive cluster of people.
- Features of puberty period.
- Psyche instability.
- Reducing blood sugar (with diabetes or strict diet).
- Brain circulation problems in old age.
- Nervous and physical exhaustion.

Types of fainting:
- Orthostatic fainting. It happens from a sharp change of body position (from horizontal to vertical). The reason may be the insufficiency of the engine device due to disorders of the function of nerve fibers – the participants of the vascular function. Fainting is dangerous falling and injury.
- Fainting caused by long immobile (especially standing). Similar to the previous type. Arises due to the lack of contraction of the muscles, full blood flow on the vessels in the legs (blood cannot overcome the power of gravity and get to the brain).
- High-altitude fainting. Arises at a high height due to bad blood supply to the brain.
- «Simple» fainting (beyond major reasons): tumping consciousness, drop pressure, intermittent breathing, short-term loss of consciousness, very fast return to normal.
- Convulsive fainting. The condition is accompanied by convulsions and (often) redness / face.
- Bettoleppsia. Short-term fainting in chronic lung disease arising due to a strong cough attack and subsequent blood outflow from the skull.
- Drop Atachi. Dizziness, severe weakness and fall without loss of consciousness. Risk factors: pregnancy, osteochondrosis of the cervical.
- Vasodepressor fainting. Arises due to a stuff, lack of sleep, fatigue, emotional stress, fright, etc. The pulse decreases below 60 ice / min, pressure drops sharply. You can often prevent fainting, just by accepting horizontal position.
- Arrhythmic fainting. Consequence of one type of arrhythmia.
- Situating faint. Occurs after defecation, constipation, diving, weight lifting, etc. Due to increasing intragenic pressure and other factors.
- Carotid sinus syndrome. Note, Carotid sinuses – Sleepy arteries, main blood suppliers to the brain. Strong pressure on these sinuses (tight collar, sharp head turn) leads to a fainting.
- Fainting in the presence of heart rhythm. It occurs with a sharp bradycardia (heart rhythm – less than 40 UD / min) or in paroxysmal tachycardia (180-200 Ud / min).
- Anemic faint. Most often occurs in the elderly because of a sharp decrease in hemoglobin, the deficiency of iron in nutrition, due to the impairment of iron absorption (when the gastrointestinal disease occurs).
- Medical faint. Happen
- Happens from intolerance / overdose of drugs.

Signs and symptoms of fainting – how to recognize a faint?
The doctors usually stand out 3 of the faint:
- Pre-corrupt. The appearance of harbingers of fainting. Condition lasts about 10-20 seconds. Symptoms: nausea, strong dizziness, lack of air, ringing in the ears and sudden weakness, unexpected weight in the legs, cold sweat and darkening in the eyes, skin pallor and numbness, rare breathing, pressure drop and weak pulse, «Mukhi» Before your eyes, Gray Skin Covers.
- Snowstanding. Symptoms: loss of consciousness, reduction of muscle tone and neurological reflexes, superficial breathing, in some cases even convulsions. The pulse is weak or not at all. Pupils Extended, Reaction to Light Reduced.
- Post-combature. The general weakness persists, consciousness returns, a sharp rise to his feet can provoke another attack.
In comparison with other types of disturbances, fainting is distinguished by the fully restoration of the state, which he preceded.
Rules for the first aid for fainting – what to do with fainting, and what do not need to do?
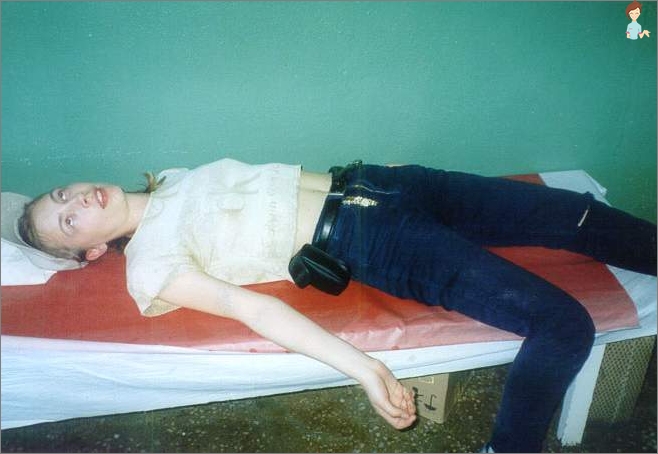
The first help to man in fainting is as follows:
- Eliminate (if there is a) fainting factor. That is, we endure (remove) a person from the crowd, close room, stuffy room (or we introduce into a cool room from the street), we carry out the road, pull out of the water, etc.
- We provide a horizontal sustainable person – The head is lower than the body, the legs are higher (for the influx of blood to the head, if there is no head injury).
- We put on the side, for the prevention of the backrest (and so that the person does not choke a vomit). If the ability to put a person is missing, we sit down and put it on the head between the knees.
- Next should cause irritation of skin receptors – to spray the face of a man with cold water, lose the ear shells, pat on the cheeks, wipe the face with a cold wet towel, ensure air flow (unzipped the collar, belt, corset, open the window), give to breathe the ammonia (vinegar) – 1-2 cm from the nose, Slightly shake Vatka.
- Warm blanket under reduced body temperature.
When a person comes to himself:
- You can not eat and drink.
- You can not immediately take a vertical position (only in 10-30 minutes).
- If a person does not come to himself:
- Urgently call ambulance.
- Check the free air intake in the respiratory tract, pulse, listen to breathing.
- If there is no pulse and breathing – we do an indirect heart massage and artificial respiration («Mouth in Roth»).
If the elderly person or a child falls into fainting, if there are serious diseases in history if the faint is accompanied by convulsions, loss of breathing, if the faint has happened without visible reasons at a flat place, suddenly – immediately call an ambulance. Even if a person quickly came to his senses, there is a risk of shaking brain and other injuries.


